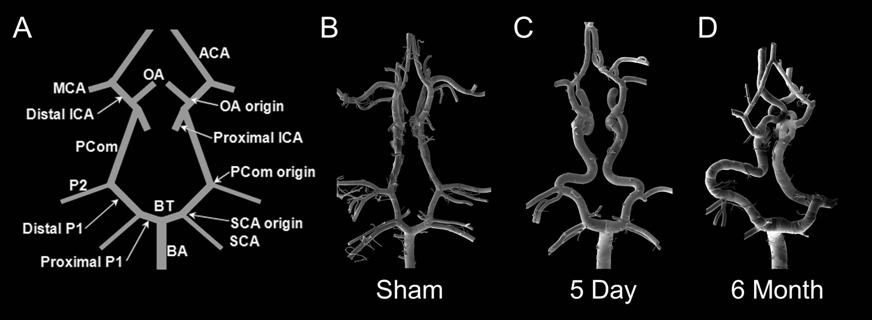
A hemodynamic model for IA formation
A wide variety of factors have been associated with IA incidence, ranging from smoking to hypertension to menopausal state in women. However, the predominance of IAs at apices of arterial bifurcations and outer curves of brain arteries suggests that the unique hemodynamics of such locations is critical in IA formation. Using hemodynamically induced aneurysm models, our lab has found that the insult from abnormal hemodynamics does in fact play a critical role in aneurysm formation.
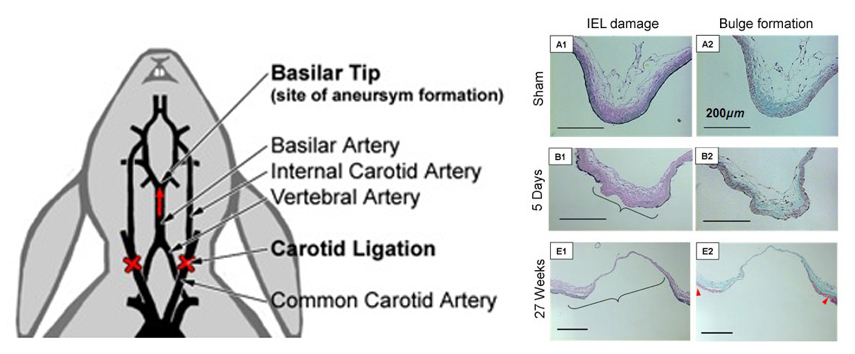
Hemodynamic insult in intracranial bifurcations
We created a rabbit basilar tip (BT) aneurysm model by increasing flow to the BT via bilateral common carotid artery (CCA) ligation. The increased hemodynamic insult alone was sufficient to cause aneurysm formation at the BT bifurcation. Following flow increase aneurysmal remodeling occurred near the apex of the BT. This damage was characterized by loss of the IEL, media thinning and bulge formation. As shown in the histological images of the BT, loss of the IEL and bulge formation progressed from 5 days out to 27 weeks.
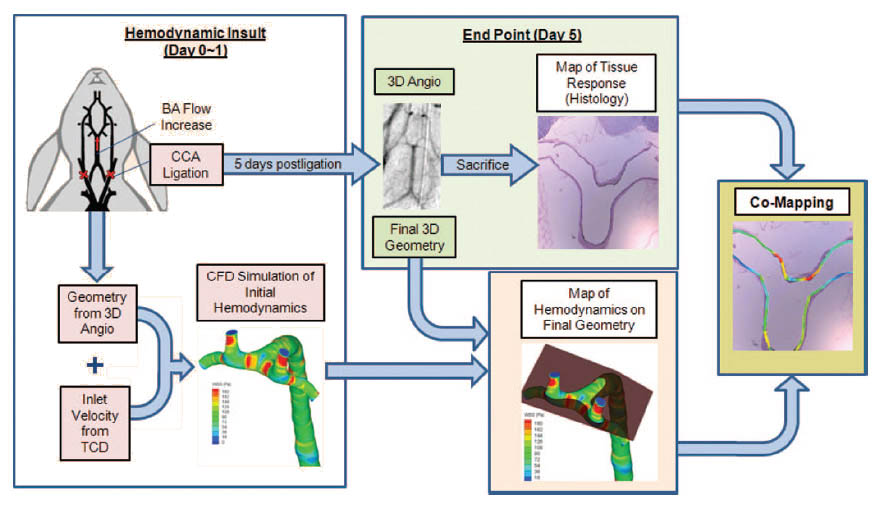
With the ability to obtain vessel geometries using 3D angiography we are able to determine hemodynamic flow fields using CFD in vessels and match changes in hemodynamics to morphological and biochemical changes of the vessel wall. A flow chart of the steps taken to perform this co-mapping of CFD with biology is outlined below. Using such technology we have boldly proposed that high hemodynamic wall shear stress (WSS) and positive WSS gradient (WSSG) induce IA formation via mal-adaptive vascular remodeling.
In order to correlate the earliest vascular damage with the responsible initial hemodynamic insult, the co-mapping procedure was employed to spatially map WSS and WSSG distributions with the IEL loss- the earliest and most consistent marker of aneurysmal damage. We found that IEL damage segregated to an areas of high WSS and positive WSSG.
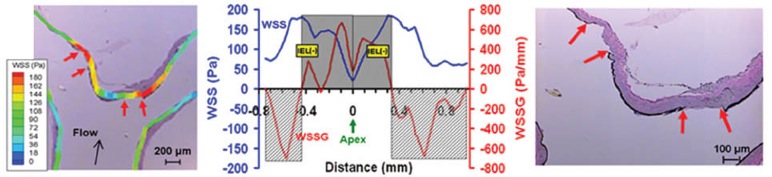
This study has identified the integral role of flow during aneurysm genesis by identifying high WSS and positive WSSG hemodyanmics as a primary initiating factor.
Molecular mechanisms of aneurysm initiation
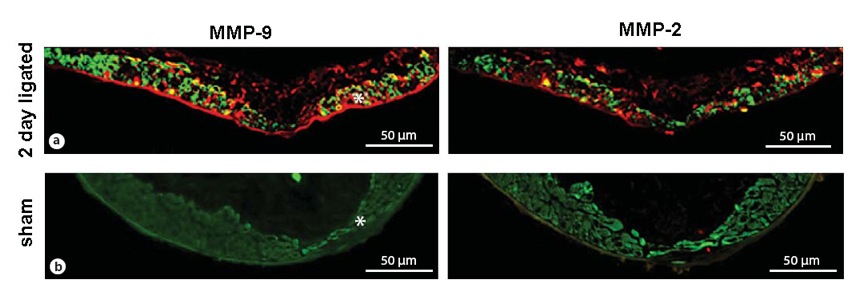
Given the development of these IA changes in the vessel wall, which are spatially consistent with high WSS and positive WSSG, we are interested in determining the molecular mechanism by which hemodynamics is translated to remodeling and destruction of the vessel wall. We have found that the members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs) family are instrumental in the degradation and remodeling that we observe in our models. For example, as shown in the image below, there are increased levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9 (red) expressed by SMCs (green, SMC marker alpha-actin) in the peri-apical region as early as 2 days after ligation. Additionally, we are looking to the role of nitric oxide, superoxide, and other oxidative species in IA formation.
Vascular corrosion casting of the Circle of Willis
Bilateral CCA ligation not only causes aneurysm formation at the BT but could also induce vascular remodeling throughout the Circle of Willis. To investigate this, we performed vascular corrosion casting on rabbits with bilateral CCA ligation, and visualized these endocasts via scanning electron microscopy. We found that as a result of altering and rerouting blood flow in the cerebral vasculature, CCA ligation has the potential to induce aneurysms in other locations of the Circle of Willis as well as other vascular pathologies. This may be important for clinicians dealing with patients with carotid artery disease, elective carotid ligation, or Moyamoya disease.
For more informtion, please contact Vincent Tutino at vincentt(at)buffalo.edu.
Recent Publications
Matthew Tutino, V., Liaw, N., Andrew Spernyak, J., Nicolae Ionita, C., Hussain Siddiqui, A., Kolega, J. & Meng, H. 2016 Assessment of vascular geometry for bilateral carotid artery ligation to induce early basilar terminus aneurysmal remodeling in rats . Current neurovascular research 13, 82-92.
Rajabzadeh-Oghaz, H., Varble, N., Davies, J.M., Mowla, A., Shakir, H.J., Sonig, A., Shallwani, H., Snyder, K.V., Levy, E.I. & Siddiqui, A.H. 2017 Computer-Assisted Adjuncts for Aneurysmal Morphologic Assessment: Toward More Precise and Accurate Approaches. In Proc. of SPIE Vol (pp. 101341C-101341.
Paliwal, N., Damiano, R.J., Davies, J.M., Siddiqui, A.H. & Meng, H. 2017 Association between hemodynamic modifications and clinical outcome of intracranial aneurysms treated using flow diverters . In Proc. of SPIE Vol (pp. 101352F-101351.
Paliwal, N., Yu, H., Xu, J., Xiang, J., Siddiqui, A.H., Yang, X., Li, H. & Meng, H. 2016 Virtual stenting workflow with vessel-specific initialization and adaptive expansion for neurovascular stents and flow diverters . Computer methods in biomechanics and biomedical engineering 19, 1423-1431
Damiano, R., Tutino, V., Paliwal, N., Ma, D., Davies, J., Siddiqui, A. & Meng, H. 2017 Compacting a Single Flow Diverter versus Overlapping Flow Diverters for Intracranial Aneurysms: A Computational Study. American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Varble, N., Xiang, J., Lin, N., Levy, E. & Meng, H. 2016 Flow instability detected by high-resolution computational fluid dynamics in fifty-six middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Journal of biomechanical engineering 138, 061009.
Xiang, J., Antiga, L., Varble, N., Snyder, K.V., Levy, E.I., Siddiqui, A.H. & Meng, H. 2016 AView: An Image-based Clinical Computational Tool for Intracranial Aneurysm Flow Visualization and Clinical Management. Annals of biomedical engineering 44 , 1085-1096. (doi:10.1007/s10439-015-1363-y).
Matthew Tutino, V., Liaw, N., Andrew Spernyak, J., Nicolae Ionita, C., Hussain Siddiqui, A., Kolega, J. & Meng, H. 2016 Assessment of vascular geometry for bilateral carotid artery ligation to induce early basilar terminus aneurysmal remodeling in rats.
Current neurovascular research 13 , 82-92
Xiang, J., Damiano, R.J., Lin, N., Snyder, K.V., Siddiqui, A.H., Levy, E.I. & Meng, H. 2015 High-fidelity virtual stenting: modeling of flow diverter deployment for hemodynamic characterization of complex intracranial aneurysms. Journal of neurosurgery, 1-9. (doi:10.3171/2014.11.JNS14497).
Damiano, R.J., Ma, D., Xiang, J., Siddiqui, A.H., Snyder, K.V. & Meng, H. 2015 Finite element modeling of endovascular coiling and flow diversion enables hemodynamic prediction of complex treatment strategies for intracranial aneurysm. Journal of biomechanics . (doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2015.06.018 ).
Xiang J, Antiga L, Varble N, Snyder KV, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH, Meng H, “ AView: An Image-based Clinical Computational Tool for Intracranial Aneurysm Flow Visualization and Clinical Management”, Ann Biomed Eng, [Epub ahead of print], 2015 Jun 23. PMID: 26101034
Damiano R, Ma D, Xiang J, Snyder KV, Meng H, “ Finite Element Modeling of Endovascular Intervention Enables Hemodynamic Prediction of Complex Treatment Strategies of Coiling and Flow Diversion”, J Biomechanics, 2015 Jun 27.
Xiang J, Damiano R, Lin N, Snyder KV, Siddiqui AH, Levy EI, Meng H, “ High-fidelity virtual stenting: modeling of flow diverter deployment for hemodynamic characterization of complex intracranial aneurysms”, Journal of Neurosurgery, [Epub ahead of print], 2015 Jun 19:1-19. PMID: 26090829 (Xiang and Damiano contributed equally to this work)
Xiang J, Damiano R, Lin N, Snyder KV, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH, Meng H, “ Flow diverters - One device does not fit all. Response”, Journal of Neurosurgery, [Epub ahead of print], 2015 Jun 19:1-3. PMID: 26090837
Xiang J, Yu J, Snyder K, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH, Meng H, “ Hemodynamic-morphological discriminant models for intracranial aneurysm rupture remain stable with increasing sample size”, J Neurointerv Surg, [Epub ahead of print], 2014 Dec 8. PMID: 25488922
Xiang J, Siddiqui AH, Meng H, “ The Effect of Inlet Waveform Boundary Conditions in Computational Hemodynamics of Intracranial Aneurysms”, Journal of Biomechanics, 47(16):3882-90, 2014. PMID: 25446264
Xiang J, Yu J, Choi H, Fox Dolan J, Snyder K, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH, Meng H, “ Rupture Resemblance Scale (RRS)?Toward Risk Stratification of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms Using Hemodynamic-Morphologic Discriminants”, J Neurointerv Surg, 7(7):490-5, 2015. PMID: 24811740
Xiang J, Ma D, Snyder K, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH, Meng, H, “ Increasing Flow Diversion for Cerebral Aneurysm Treatment Using a Single Flow Diverter”, Neurosurgery, 75(3):286-94, 2014. PMID: 24867201
Ma D, Xiang J, Choi H, Natarajan S, Dumont TM, Siddiqui AH, Meng H, “ Enhanced Aneurysm Flow Diversion using Dynamic Push-Pull Technique: An Experimental and Modeling Study”, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 35(9):1779-85, 2014. PMID: 24763414
Xiang J, Tutino V, Snyder K, Meng H, “ CFD: Computational Fluid Dynamics or Confounding Factor Dissemination? The Role of Hemodynamics in Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture Risk Assessment”, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, [Epub ahead of print], 2013 Sep 12. PMID: 24029393
Liu J, Xiang J, Ma D, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Li H, Meng H, “ Morphologic and Hemodynamic analysis of paraclinoid aneurysms: ruptured vs unruptured”, J Neurointerv Surg,6(9):658-63, 2014. PMID: 23598838
Meng H, Tutino VM, Xiang J, Siddiqui A, “High WSS or Low WSS? Complex Interactions of Hemodynamics with Intracranial Aneurysm Initiation, Growth, and Rupture: Toward a Unifying Hypothesis”, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 35(7):1254-62, 2014. PMID: 23598838
Dolan JM, Kolega J, Meng H, “High Wall Shear Stress and Spatial Gradients in Vascular Pathology: A Review”, Annals of Biomedical Eng, 41(7):1411-27, 2013. PMID: 23229281
Ma D, Dargush GF, Natarajan SK, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH, Meng H, “Computer modeling of deployment and mechanical expansion of neurovascular flow diverter in patient-specific intracranial aneurysms”, J Biomech., 45: 2256-63, 2012. PMID: 22818662
Xiang J, Tremmel M, Kolega J, Levy EI, Natarajan SK, Meng H, “Newtonian viscosity model could overestimate wall shear stress in intracranial aneurysm domes and underestimate rupture risk”, J Neurointerv Surg., 4: 351-7, 2012. PMID: 21990529
Kolega J, Gao L, Mandelbaum M, Natarajan SK, Mocco J, Siddiqui AH, Meng H, "Cellular and molecular responses of the basilar terminus to hemodynamics during intracranial aneurysm initiation in a rabbit model", J Vasc Res., 48: 429-442, 2011. PMID: 21625176
Dolan JM, Meng H, Sigh S, Paluck RA, Kolega J, "High Fluid Shear Stress and Spatial Shear Stress Gradients Affect Endothelial Proliferation, Survival, and Alignment", Annals of Biomedical Eng, 39: 1620, 2011. PMID: 21312062
Xiang J, Natarajan SK, Tremmel M, Ma D, Mocco J, Hopkins LN, Siddiqui AH, Levy EI and Meng H, "Hemodynamic Morphological Discriminants for Intracranial Aneurysms Rupture", Stroke, 42:144-152, 2011. PMID: 21106956
Meng H, Metaxa E, Gao L, Liaw N, Natarajan SK, Swartz DD, Siddiqui AH, Kolega J, Mocco J, "Progressive Aneurysm Development Following Hemodynamic Insult", J Neurosurg., 114: 1095-1103, 2011. PMID: 20950086
Tanweer O, Metaxa E, Liaw N, Sternberg DS, Siddiqui AH, Kolega J, Meng H, "Inhibition of Stretch-activated Ion Channels on Endothelial Cells Disrupts Nitric Oxide-mediated Arterial Outward Remodeling", J Biorheology, 24:77-83, 2010.
Tremmel M, Xiang J, Natarajan SK, Hopkins LN, Siddiqui AH, Levy EI, Meng H, "Alteration of Intra-aneurysmal Hemodynamics for Flow Diversion Using Enterprise and Vision Stents", World Neurosurgery, 74:306-315, 2010. PMID: 21197155
Metaxa E, Tremmel M, Natarajan SK, Xiang J, Paluch RA, Mandelbaum M, Siddiqui AH, Kolega J, Mocco J, Meng H, "Characterization of Critical Hemodynamics Contributing to Aneurysmal Remodeling at the Basilar Terminus in a Rabbit Model", Stroke, 41:1774-1782, 2010 (Featured on Cover of Stroke, August 2010 issue). PMID: 20595660
Tremmel M, Xiang J, Hoi Y, Kolega J, Siddiqui AH, Mocco J, Meng HNeurosurgery, "Mapping Vascular Response to In Vivo Hemodynamics: Application to Increased Flow at the Basilar Terminus", Biomech Model Mechanobiol., 9: 421-434, 2010. PMID: 20054605
Rahman M, Smietana J, Hauck EF, Hoh B, Hopkins LN, Siddiqui AH, Levy EI, Meng H, Mocco J, "Size Ratio Correlates with Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture Status: A Prospective Study", Am Stroke, 41:916-920, 2010. PMID: 20378866
Meng H, Natarajan SK, Gao L, Ionita C, Kolega J, Mocco J, Siddiqui AH, "Aneurysmal Changes at the Basilar Terminus in the Rabbit Elastase Aneurysm Model", AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 31:300-3. 2010. PMID: 20053800
Ma D, Tremmel M, Paluch R, Levy EI, Meng H, Mocco J, "Size Ratio for Clinical Assessment of Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture Risk", Neurol Res., 32: 482-486, 2010. PMID: 20092677
de Jong J, Salazar J, Woodward SH, Collins LR, Meng H, "Measurement of inertial particle clustering and relative velocity statistics in isotropic turbulence using holographic imaging", Int J Multiphase Flow , 36:324-332, 2010.